
Link:https://m.huanqiu.com/article/4FQry5fMTDy
Sand mining, a linchpin of construction and infrastructure development, stands as a pivotal force propelling economic growth. In Sierra Leone, a nation marked by rapid urbanization and ambitious infrastructural endeavors, sand mining has taken center stage as a foundational industry. This surge, however, comes with a set of pressing environmental and social considerations. It calls for a comprehensive evaluation of its ramifications and the development of robust strategies for sustainable stewardship.
As the demand for housing, roads, and other structures skyrockets, sand mining becomes an indispensable component of the construction landscape. It provides the raw material essential for concrete production, making it a driving force behind Sierra Leone's economic expansion. The construction industry, in turn, fuels employment opportunities and stimulates economic activity, creating a ripple effect of prosperity. Yet, this surge in sand mining activity has not come without its challenges. Unregulated or poorly managed extraction practices can lead to habitat destruction, altered riverbeds, and erosion of coastal areas. Furthermore, the depletion of sand can have severe consequences on local ecosystems, affecting aquatic life and potentially exacerbating the impacts of natural disasters.
In tandem with these environmental concerns, social implications loom large. The industry can bring about land tenure conflicts, displacement of communities, and socio-economic disparities if not managed with foresight and care. Balancing the urgent need for economic development with the imperative of environmental and social preservation is the crux of achieving sustainable sand mining practices in Sierra Leone. Strategic interventions, such as effective regulation, community engagement, and investment in research and innovation, will be instrumental in navigating this complex terrain. Through a holistic and forward-thinking approach, Sierra Leone can ensure that the benefits of sand mining are harnessed without compromising the long-term well-being of its people and precious natural resources.
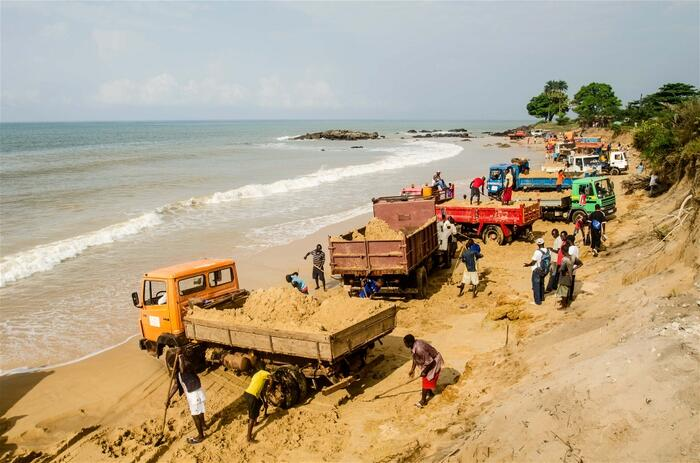

Source: https://reliefweb.int/report/sierra-leone/sand-mining-threatens-homes-and-livelihoods-sierra-leone
Environmental Impacts
Unregulated sand mining in Sierra Leone has unleashed far-reaching environmental consequences. The very areas that provide natural flood protection and regulate sedimentation patterns, riverbanks, and coastal zones, are now facing a perilous threat. This jeopardizes not only the structural integrity of these vital environments but also the delicate equilibrium of entire ecosystems.
Erosion, an immediate consequence of unregulated sand mining, erodes the resilience of riverbanks. These natural barriers, crucial in shielding communities against flooding, are gradually undermined. This leaves settlements vulnerable to the destructive forces of inundation, imperiling human habitats and the livelihoods of those dependent on these fertile riverbanks for agriculture.
Furthermore, alterations in natural processes wreak havoc on ecosystems, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic habitats. Aquatic environments, sensitive to changes in sedimentation patterns, bear the brunt of this disruption. The finely tuned balance that supports a diverse range of aquatic life is thrown into disarray. Species adapted over millennia struggle to adapt to these rapid and drastic alterations.
Terrestrial habitats also bear the brunt of unregulated sand mining. Stable riverbanks, essential for a plethora of flora and fauna, face depletion. Riparian vegetation, specialized to thrive at the interface of land and water, faces a decline. This not only affects the plant species directly but reverberates through the ecosystem, impacting the entire food chain.
Most crucially, unregulated sand mining directly threatens biodiversity. The extraction process often leads to the destruction of aquatic habitats, spelling disaster for fish species and other wildlife. The intricate relationships between various organisms in these habitats are disrupted, resulting in a decline in crucial fish populations. This has implications not only for the local fishing industry but also for broader food security and economic stability.
Source: https://www.worldatlas.com/maps/sierra-leone
Social Implications
Sand mining in Sierra Leone carries substantial social implications beyond its environmental impacts. Disputes over land rights and conflicts between various stakeholders have surged, particularly in regions where sand mining activities are concentrated. These disputes arise from the coexistence of traditional, informal land tenure systems with formal legal frameworks. Such complexities escalate conflicts over ownership and usage rights, leading to protracted legal battles and, in some instances, even violence. This not only strains social relations within affected communities but also poses a challenge to local governance and law enforcement.
Moreover, conflicts between different stakeholders, including communities, government authorities, and mining companies, have become increasingly prevalent. Divergent interests and priorities often collide, heightening tensions. Communities residing near extraction sites are acutely aware of the impact of mining on their surroundings and seek to safeguard their interests. In contrast, mining companies, driven by economic imperatives, may focus on maximizing extraction efficiency. Resolving these conflicts requires transparent decision-making processes and a commitment to equitable resource distribution.
The livelihoods of communities near sand mining operations are intricately linked to the industry. Many rely on the extraction of sand for direct employment, often engaging in activities such as manual extraction, transportation, or related services. The industry's prosperity directly influences the economic well-being of these communities. However, unregulated or unsustainable mining practices can lead to long-term job insecurity. Environmental degradation resulting from over-mining can compromise the viability of livelihoods tied to the natural resource base.
In conclusion, the social implications of sand mining in Sierra Leone are profound. Disputes over land rights, conflicts between stakeholders, and the livelihoods of affected communities are central concerns. Recognizing and addressing these social dimensions are imperative for achieving sustainable development in the context of sand mining. Cooperation between government, industry, and local communities is essential to strike a balance between economic growth and the well-being of the affected population. By prioritizing the social dimensions of sand mining, Sierra Leone can ensure that the industry contributes positively to the overall welfare and prosperity of its communities.
Regulatory Frameworks
Robust regulatory frameworks play a vital role in steering the sand mining industry towards sustainability. By establishing effective governance and oversight, Sierra Leone can ensure that extraction activities align with established environmental standards, mitigating potential harm to natural ecosystems. This involves bolstering monitoring and enforcement mechanisms and employing tools like satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to track operations.
Furthermore, collaboration between regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders is crucial in crafting and executing policies that strike a harmonious balance between economic progress and environmental preservation. This cooperative approach fosters a sense of shared responsibility and facilitates the integration of diverse perspectives, ultimately resulting in more comprehensive and effective regulations.
A proactive regulatory framework not only safeguards the environment but also engenders trust within the industry and among local communities. It provides a clear roadmap for responsible sand mining practices, assuring both stakeholders and the public that the industry is operating with diligence and care.
In conclusion, the establishment of sound regulatory frameworks is instrumental in steering the sand mining industry towards a sustainable future. Through effective governance, monitoring, and collaborative policy-making, Sierra Leone can ensure that economic development is pursued in harmony with the conservation of its invaluable natural resources. This balanced approach paves the way for a more prosperous and environmentally-resilient future.
Community Engagement
Empowering local communities stands as a cornerstone in promoting responsible resource management. In order to establish a framework that is both sustainable and equitable, it is imperative to integrate local perspectives, and traditional wisdom, and uphold land rights. By recognizing the invaluable insights that communities possess about their own environments, we create a collaborative environment where the impacts and benefits of sand mining are fairly distributed.
Transparent and inclusive community engagement is paramount. It ensures that decisions about sand mining activities are made collectively, with the interests and concerns of the local populace at the forefront. This process not only builds trust but also aligns the industry's objectives with the long-term well-being of the communities.
Furthermore, this engagement goes beyond immediate stakeholders; it extends to future generations who will inherit the outcomes of today's decisions. By involving communities in a meaningful way, we establish a legacy of sustainable resource management that transcends short-term gains.
In conclusion, genuine community engagement is not only a fundamental ethical consideration but a pragmatic necessity for the responsible management of sand mining. It is through this collaborative approach that we can strike a balance between economic progress and the preservation of the social and environmental fabric of Sierra Leone.
Research and Innovation
Investment in research and innovation holds the key to transforming the sand mining industry towards sustainability. Sierra Leone must focus on diversifying its strategies, which encompasses investigating alternative construction materials, integrating cutting-edge mining technologies, and embracing ecological restoration methods. These initiatives collectively promise a reduction in the environmental impact of sand mining, safeguarding the delicate ecosystems surrounding extraction sites. Through scientific advancements, it is possible to identify materials and techniques that are not only more environmentally friendly but also economically viable. Furthermore, the implementation of advanced mining technologies enhances efficiency while minimizing resource wastage. By prioritizing research and innovation, Sierra Leone can strike a harmonious balance between economic development and environmental conservation, ensuring a prosperous and sustainable future for both the sand mining industry and the broader construction sector.
Socio-Economic Benefits
The sand mining industry in Sierra Leone harbors substantial potential for socio-economic advancement. When handled sustainably, it becomes a dynamic force propelling economic growth, employment opportunities, and infrastructural enhancement. Profits garnered from sand mining can be strategically reinvested into local communities, acting as a financial backbone for critical services like education, healthcare, and public infrastructure. This infusion of capital not only elevates living standards but also fosters a conducive environment for overall development.
Furthermore, the industry acts as a fertile ground for entrepreneurship, particularly through small-scale sand extraction operations. This empowers local individuals and communities to actively participate in economic activities, thereby strengthening and diversifying the economic landscape. As these ventures proliferate, they contribute to the resilience and self-sufficiency of the region's economy.
However, it is imperative that these benefits are reaped in a manner that harmonizes with ecological and social considerations. Responsible and sustainable practices are key to ensuring that the socio-economic advantages of the sand mining industry in Sierra Leone are not overshadowed by adverse environmental impacts or socio-cultural disruptions. With careful management, this industry can serve as a cornerstone for holistic progress and prosperity in the region (see, Table1)
Table 1: Stakeholders in Sierra Leone’s sand governance
Stakeholder |
Decisional level |
Value chain stage |
MMMR |
National |
Transversal/centralized |
EPA |
National |
Transversal/centralized |
Extraction & construction companies |
Global |
Primary source; Secondary sources; Initial processing, trade, and transport |
Local authorities |
Local |
Primary source; Initial processing, trade, and transport |
Village Chiefs |
Local |
Primary sources; Initial processing, trade, and transport |
Artisanal mining community |
Local |
Primary sources; Initial processing, trade, and transport |
Foreigner community |
Local |
Demand sectors & uses |
Source: (Authors’ compilation, 2021)
Technological Innovations:
In the pursuit of sustainable sand mining practices, the integration of cutting-edge technology is paramount. Advanced monitoring systems, like satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), play a pivotal role in overseeing extraction operations and assessing alterations in land use patterns. These technologies provide a comprehensive and real-time view of mining activities, enabling regulators and stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate data.
Moreover, the adoption of eco-conscious extraction techniques represents a significant stride towards sustainability. Methods such as suction dredging and conveyor systems not only enhance operational efficiency but also substantially diminish habitat disruption and minimize the industry's overall ecological impact. Suction dredging, for instance, allows for precise and controlled extraction, reducing collateral damage to surrounding ecosystems.
By leveraging these technological innovations, the sand mining industry can strike a harmonious balance between economic pursuits and environmental stewardship. It fosters a responsible approach to resource utilization, safeguarding natural habitats and biodiversity while meeting the demands of construction and infrastructure development. Embracing these advancements is not only a progressive step for the industry but also a testament to the potential of human ingenuity in creating sustainable solutions for pressing environmental challenges.
International Cooperation:
In the context of environmental issues, particularly those with cross-border implications, international cooperation is of paramount importance. Sierra Leone stands to gain immensely from engaging with neighboring nations and international organizations in a concerted effort to exchange knowledge and promote sustainable sand mining practices. By doing so, the country can tap into a wealth of expertise, accessing best practices that have proven successful elsewhere.
This collaborative approach extends beyond practical considerations. It fosters regional stability and prosperity, as nations work together towards a common goal of sustainable resource management. Moreover, it demonstrates a shared commitment to environmental conservation that transcends political boundaries.
Through international cooperation, Sierra Leone not only fortifies its own efforts towards sustainable sand mining but also contributes to a global ethos of responsible resource utilization. It sets a precedent for collaborative problem-solving in the face of complex environmental challenges. Ultimately, this approach not only benefits Sierra Leone but also serves as an exemplar of international solidarity and collective action in safeguarding our planet's natural resources for future generations.
Diversification of Economic Activities:
Diversification of economic activities is crucial for long-term stability and sustainable development. While the sand mining industry plays a pivotal role in Sierra Leone's economy, over-reliance on any one sector can pose risks. To mitigate this, Sierra Leone should actively seek out opportunities for economic diversification.
Investing in renewable energy presents a promising avenue. The development of solar, wind, and hydroelectric projects not only reduces environmental impact but also fosters a transition towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. This not only addresses energy needs but also positions Sierra Leone as a regional leader in renewable technology.
Agriculture offers another avenue for diversification. By supporting and modernizing the agricultural sector, Sierra Leone can boost food security, create employment opportunities, and enhance export potential. Furthermore, sustainable agricultural practices can contribute to conservation efforts and promote ecological resilience.
Tourism is yet another sector with vast potential. Sierra Leone's natural beauty, diverse culture, and historical sites hold considerable appeal for international travelers. Thoughtful and sustainable tourism development can generate revenue, create jobs, and foster cultural exchange while preserving the nation's natural and cultural heritage.
By diversifying its economic activities, Sierra Leone not only safeguards against overdependence on a single industry but also builds a more resilient, adaptable economy. This strategy ensures that the country can weather fluctuations in global sand demand and thrive in a rapidly changing economic landscape, ultimately securing a prosperous and sustainable future.
Education and Awareness Campaigns:
Education and awareness campaigns are pivotal tools in promoting sustainable resource management. They empower communities and industry stakeholders with the knowledge and understanding needed to actively participate in conservation efforts. By instilling a sense of responsibility and environmental stewardship, these campaigns cultivate a culture of conscious citizenship.
It is essential that such initiatives target a diverse audience. Local communities, being directly impacted by resource extraction, must be well-informed about the potential consequences and sustainable practices. Industry professionals play a critical role in implementing these practices, making it imperative that they are well-versed in sustainable techniques. Policymakers, too, need to be educated to formulate and enforce regulations that prioritize sustainability.
Moreover, the general public must be engaged, as they constitute a powerful force for change. Through education, individuals become advocates for responsible resource utilization, applying pressure on industries and governments to adopt sustainable practices.
By disseminating knowledge through comprehensive education and awareness campaigns, Sierra Leone can foster a collective commitment to safeguarding its natural resources. This, in turn, establishes a foundation for a more sustainable and harmonious coexistence between industry, communities, and the environment, ensuring a prosperous future for generations to come.
Long-term Planning and Monitoring:
To achieve sustainable sand mining, Sierra Leone must adopt a forward-looking approach. Establishing robust monitoring and evaluation systems is crucial in tracking the effectiveness of sustainability measures. Regular assessments should scrutinize the impact of regulations, community engagement, and technological interventions. This iterative process enables adaptive management, where strategies are honed in response to real-time feedback and evolving conditions.
By implementing these strategies, Sierra Leone can successfully navigate the intricate landscape of sand mining. This will allow for a delicate equilibrium between economic advancement and environmental conservation. Through steadfast dedication to sustainability, coupled with collaboration and innovation, Sierra Leone can forge a path toward a future where the benefits of sand mining are harnessed without jeopardizing the long-term well-being of its citizens and the invaluable natural resources they rely on. This approach not only secures prosperity in the present but also lays the foundation for a sustainable legacy that will benefit generations to come.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic context of Sierra Leone, the prudent management of sand mining emerges as a complex endeavor. Yet, with the implementation of robust regulatory frameworks, active community engagement, the adoption of sustainable practices, and substantial investment in research and innovation, Sierra Leone stands poised to reconcile the imperatives of economic progress with environmental preservation.
By harnessing the potential of the sand mining industry in a conscientious and sustainable manner, Sierra Leone not only secures its economic well-being but also lays the groundwork for a future characterized by inclusive prosperity, interconnectivity, and enduring sustainability. This balanced approach ensures that economic growth is not pursued at the expense of the environment, safeguarding the ecological integrity that underpins the nation's long-term prosperity.
This path forward requires a concerted effort from stakeholders across the spectrum — from government bodies to industry players, local communities to environmental advocates. Together, they can forge a new paradigm that not only maximizes the benefits of sand mining but also safeguards the natural heritage of the nation for generations to come.
It is in this harmonious convergence of economic vitality and ecological stewardship that Sierra Leone can chart a course toward a future that honors the delicate balance between human advancement and the preservation of our planet's invaluable resources. This vision not only envisions a thriving economy but also a legacy of responsible resource management that future generations can inherit with pride and gratitude. By embracing this holistic approach, Sierra Leone can become a beacon of sustainable development, setting a commendable example for nations around the world.
References
https://pulitzercenter.org/stories/sierra-leone-sand-mining-whos-benefiting-and-what-cost-environment#:~:text=In%20Sierra%20Leone%2C%20the%20resource,sustainability%20problems%20and%20equity%20concerns.
Da, S., & Le Billon, P. (2022). Sand mining: Stopping the grind of unregulated supply chains. The Extractive Industries and Society, 10, 101070.
https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/pt/354291578288053592/pdf/Sierra-Leone-Economic-Diversification-Study.pdf
https://unepgrid.ch/storage/app/media/Publications/4.%20FINAL_GSOI-GSA-2022- 004_Sierra%20Leone.pdf
https://pulitzercenter.org/projects/sand-mining-sierra-leone-whos-benefiting
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/30695889.pdf
https://unepgrid.ch/storage/app/media/Publications/4.%20FINAL_GSOI-GSA-2022-004_Sierra%20Leone.pdf
https://www.worldatlas.com/maps/sierra-leone
https://www.thenewhumanitarian.org/news/2013/02/01/sand-mining-threatens-homes-and-livelihoods-sierra-leone